
A transformer is an electrical device that changes voltage and alternating current without changing the frequency. In simpler words, the transformer can step up or down the voltage of the electricity. This device plays a very important role in the transmission and distribution of electricity around the world. The transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. There are different types of transformers, which are used in different industries depending on the type of application. In this article, we will discuss the definition of transformer, its importance in power networks, its types according to application, etc. I hope this article is useful for you.
A transformer is an electrical device that is used to convert alternating voltage from one level to another. This voltage conversion can be increasing or decreasing, depending on the needs of the power grid or the devices connected to it. Transformers play a very vital role in the transmission and distribution of electricity, and without them, it will not be possible to efficiently transfer electricity from power plants to end consumers.
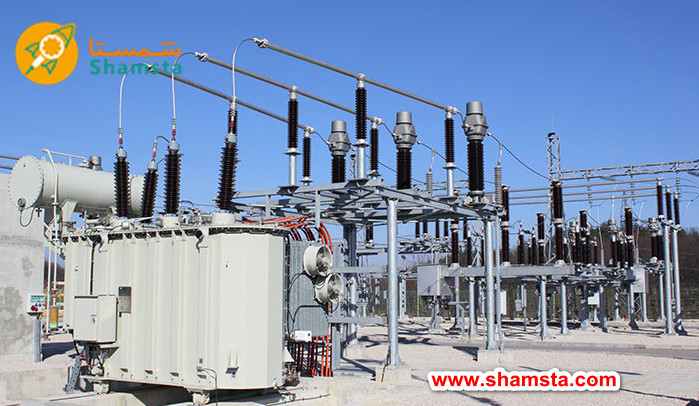

The history of the transformer goes back to the 19th century and its evolution is the result of the efforts and research of many scientists and engineers. In the following, we review the key steps in the development of transformers:
1831: Michael Faraday, a British scientist, discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction. He showed that changes in the magnetic field can induce an electric current in a coil. This discovery formed the basis of the work of transformers.
1876: Pavel Yabelkov, a Russian engineer, used a device similar to a transformer for electric lighting for the first time.
1878: Lucien Gallard and John Dixon Gibbs, British engineers, designed a device capable of transmitting electrical energy over long distances. This device, a forerunner of today's transformers, used primary and secondary windings to change voltage.
1885: William Stanley, an American engineer working for the Westinghouse Company, built the first practical and commercially usable transformer. This transformer was able to transfer electrical energy with high efficiency to long distances.
1891: At the International Electricity Exhibition in Frankfurt, for the first time, a transformer was used to transmit electricity to a distance of 175 km. This success showed that transformers can effectively transmit electricity over long distances.
In the 1970s and after: research on solid state transformers began. These types of transformers use semiconductors instead of coils and can provide additional capabilities such as precise control of voltage and frequency.
Early 20th century: As technology advanced and needed larger and more efficient power systems, transformers also improved. The use of better materials for cores and windings, as well as more advanced designs, increased the efficiency and reliability of transformers.
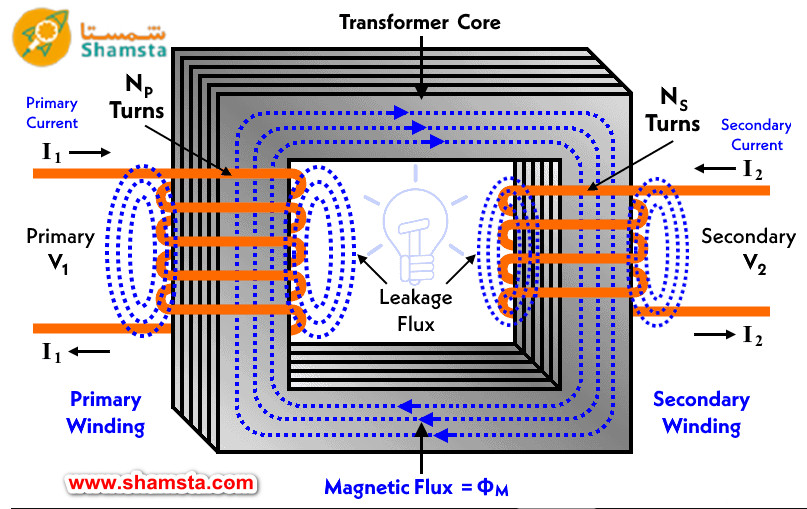
The work of the transformer is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. More simply, when an alternating current pass through a coil, an alternating magnetic field is produced. If another coil is located near this magnetic field, a voltage will be induced in that coil as well.
A) Generation of magnetic field: When an alternating current pass through the primary coil, an alternating magnetic field is created in the core.
b) Voltage induction in the secondary winding: The alternating magnetic field in the core induces an alternating voltage in the secondary winding.
c) Ratio of voltages: The ratio of primary and secondary winding voltages is almost equal to the ratio of the number of turns of the windings.
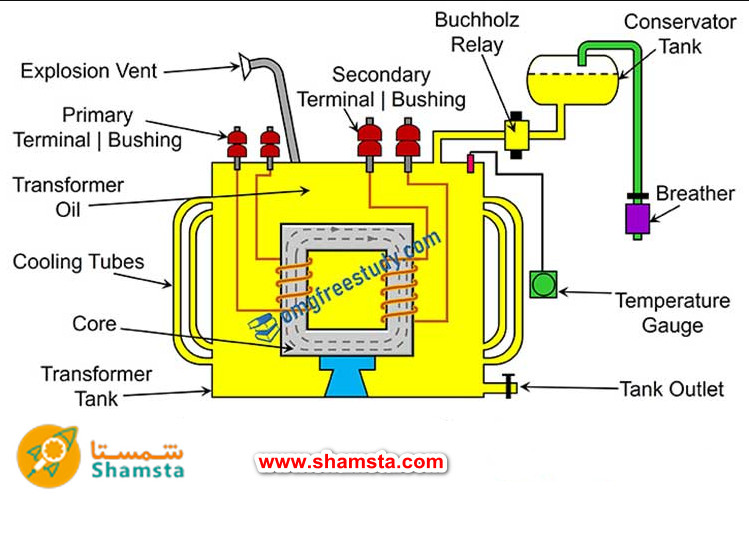
Transformers are composed of various components, each of which plays a specific role in the overall operation of the device. Next, we introduce and explain the main components of transformers:
Core : The core of the transformer is made of ferromagnetic materials such as iron or steel and is responsible for guiding the magnetic field. Cores are usually made in two ways
A) Laminated cores: which are made of thin iron sheets to reduce eddy current losses
b) Integrated cores (Solid Core): which are rarely used and are usually used in small transformers
Windings : Windings are divided into two main categories
A) Primary Winding: which is connected to the power source and alternating electric current passes through it.
b) Secondary winding: which is connected to the load and the voltage induced in it supplies the load.
c) Coils are usually made of copper or aluminum and the number of turns determines the input and output voltage.
Tank : The tank is a chamber where the core and coils are placed. This chamber is usually filled with transformer oil to provide better cooling and insulation. The oil also helps dissipate the heat generated in the core and windings
Transformer Oil : Transformer oil is used as an electrical insulation and cooling. This oil can absorb heat from the core and windings and transfer it to the tank walls, where the heat is transferred to the environment
Bushings : Bushings are insulators that allow the windings to exit the transformer housing and connect to the external power system, without contacting the metal body of the transformer. Bushings are made of insulating materials such as porcelain or heat-resistant plastics.
Radiators : Radiators are used in larger transformers to improve the cooling process. These parts connect to the tank and increase the contact surface of the oil with the air to dissipate more heat
Pressure Relief Valves : Pressure relief valves are used to prevent the internal pressure of the transformer from increasing excessively in the event of an error or temperature increase. These valves can automatically release excess pressure to prevent damage to the transformer.
Thermostats and Temperature Sensors : Thermostats and temperature sensors are used to monitor the internal temperature of the transformer and prevent excessive temperature increase. These sensors are connected to protection systems that turn off the transformer or activate additional cooling if needed.
Oil Level Indicator: These indicators are used to monitor the oil level inside the transformer. The oil level should be checked regularly to avoid oil shortage and damage to the transformer
Voltage Transformer or VT for short is a special type of transformer that is used to measure high voltages and transfer them to a safer and measurable level. This type of transformer is usually used in power systems and protection and control equipment. Transformers are divided into several main categories based on how they convert voltage
:Step-up Transformer
This type of transformer increases the input voltage. These transformers are usually used in power plants to step up the generated voltage for transmission over long distances.
: Step-down transformer
This transformer reduces the input voltage. This type of transformer is widely used in power distribution stations to convert the high voltage of transmission into a suitable voltage for domestic and industrial consumers.
: Isolation Transformer
This transformer does not actually change the input and output voltage and is only used to isolate different parts of the circuit. These transformers are used to prevent noise transmission and increase safety.
:Autotransformer
This type of transformer has only one winding, a part of which acts as a primary winding and a part as a secondary winding. This transformer can act as a voltage increaser or decreaser and is used in applications that require slight changes in voltage.
: Distribution Transformer
This step-down transformer is used to distribute electrical energy to end consumers. These transformers are usually installed near consumers.
: Frequency Transformer
This transformer not only changes the voltage but also the frequency. It is usually used in special industrial applications.
Each of these transformers are used in different places of power transmission and distribution systems, depending on the specific needs of power networks and consumers.
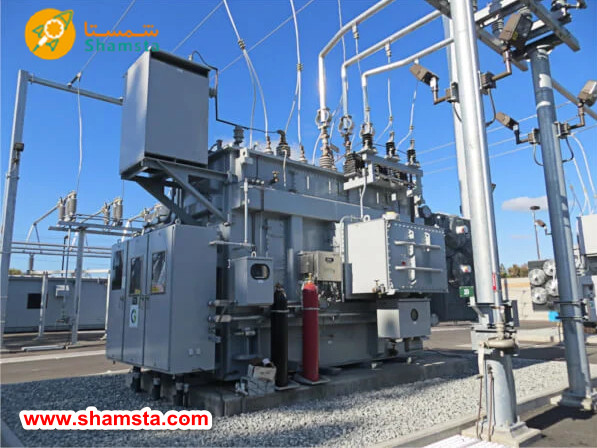

Transformers are divided into several categories based on the type and number of windings. Below are the main types of transformer based on the coil
: Two-Winding Transformer
This type of transformer consists of two separate windings: the primary winding which is connected to the voltage source and the secondary winding which provides the output voltage. This type of transformer is used for voltage conversion and electrical separation between two circuits.
: Autotransformer
In this type of transformer, there is only one coil, part of which acts as the primary coil and another part as the secondary coil. This transformer is smaller and cheaper due to the use of a common winding, but provides less electrical isolation between the input and output.
: Multi-Winding Transformer
This transformer has more than two windings and is used to convert voltage to several different levels. It is usually used in applications that need to supply different voltages, such as regulated power supplies
:Three-Phase Transformer
This type of transformer includes three primary windings and three secondary windings, which are used to convert electrical energy in three-phase systems. This transformer is widely used in industrial power networks.
:Push-Pull Transformer
This transformer has two primary windings that are symmetrically connected to the power supply. This type of transformer is used in high frequency electronic circuits and switching applications.
:Split-Core Transformer
This type of transformer has a core that can be easily removed to allow installation of the coil without cutting the cable. This transformer is commonly used in current measurement applications, such as current transformers (CT).
:Coupling Transformer
This transformer consists of several coils that are specifically designed to transfer electrical signals between different circuits. This type of transformer is used in telecommunication and data transmission equipment.

Transformers are divided into several categories based on the type of core used in their structure. Each of these cores has its own characteristics and applications
: Iron Core Transformer
This type of transformer has a core made of thin iron sheets that are stuck together. Iron core is widely used in power and distribution transformers due to its high ability to transfer magnetic flux and reduce losses.
: Steel Core Transformer
In this type of transformer, the core is made of steel, which has a higher resistance to eddy current. These transformers are used in applications that need to reduce losses and increase efficiency.
: Transformer with ferrite core (Ferrite Core Transformer)
The core of these transformers is made of ferrite materials that have high electrical resistance and are suitable for high frequencies. This type of transformer is commonly used in electronic applications, such as switching power supplies and high frequency circuits.
: Air Core Transformer
This type of transformer has a core of air or free space and therefore has no core losses. These transformers are usually used at very high frequencies and in applications that require fast and accurate response.
: Transformer with magnetic alloy core (Amorphous Core Transformer)
The core of this transformer is made of amorphous magnetic alloys, which have very good magnetic properties and reduce core losses significantly. These transformers are used in power networks with the aim of improving efficiency and reducing energy losses.
: Powdered Iron Core Transformer
The core of this transformer consists of iron powder, which are stuck together with glue or resin. This type of core is suitable for applications with high frequencies and the need for thermal stability, such as RF circuits and filters.
: Nanocrystalline Core Transformer
This transformer has a core of nanocrystalline material that has very low losses and is used for precise and high-performance applications.
These types of transformers are used in various applications from power transmission systems to electronic circuits based on the type of core used in them. Each type of core gives special characteristics and advantages to the transformer, which are selected depending on the needs of the intended application.
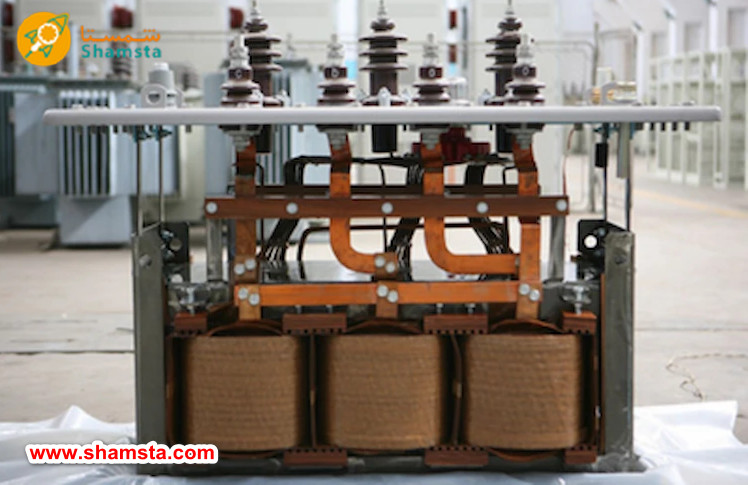

Transformers are divided into several categories based on the type of insulation used in their structure. The type of insulation used in the transformer has a great impact on its performance, safety and application:
: Oil-Immersed Transformer
In this type of transformer, the windings and core are inside a tank filled with insulating oil. In addition to being an insulator, oil is also responsible for cooling the internal parts. This type of transformer is usually used in high voltage power grids and in industrial applications.
: Dry-Type Transformer
This type of transformer uses solid insulation such as resin or air instead of oil. Dry transformers are suitable for installation in closed places and urban environments or buildings due to the absence of flammable liquids. These transformers are divided into two main categories:
Cast Resin Transformer: The windings in this type of transformer are covered with epoxy resin, which creates strong insulation and protection against moisture and pollution.
Air-Cooled Transformer: In this type, the coils are in the air and are cooled by air flow.
: Gas-insulated transformer
In this type of transformer, insulation is done by gases such as SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride). This type of transformer is used in small spaces and high voltage applications, such as urban and underground substations, due to its strong insulation and excellent cooling.
: Solid-insulated transformer
This type of transformer uses solid insulation such as insulating paper or polymers. Solid-insulated transformers are commonly used in electronic devices and small and light applications.
: Transformer with paper insulation (Paper-Insulated Transformer)
This type of transformer uses paper as an insulating material. Paper is usually mixed with oil to increase its insulating properties. This type of insulation is used in large and high voltage transformers
: Mica-Insulated Transformer
Mica is a mineral with excellent insulating properties and is used in transformers with special needs, such as high voltage and high temperature transformers.
These types of transformers are designed and manufactured based on the type of insulation for specific applications in various industries and power networks. The type of insulation used in the transformer has a direct effect on its performance, safety, cost and lifespan
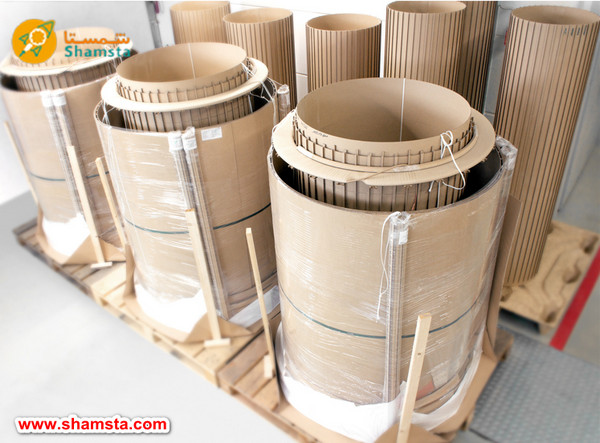

Transformers are divided into several categories based on core design. The design of the core has a great influence on the efficiency, dimensions, and application of the transformer. Below are the main types of transformer based on core design
: Toroidal Core Transformer
This type of transformer has a ring or donut shaped core. The windings are wound around this toroidal core. This design reduces magnetic losses and increases efficiency. Toroidal transformers are usually smaller and lighter than other types and are used in electronic devices and audio equipment.
: Laminated Core Transformer
The core of this transformer is made of thin metal sheets that are stuck together. These layers are insulated to reduce eddy current losses. This type of core is used in power and distribution transformers and is very popular due to its high efficiency and reduced magnetic losses.
: C-Core Transformer
In this type of transformer, the core is made in the shape of C. This design usually consists of two C-shaped pieces with coils in the middle. C core is used in special applications such as high power transformers due to the reduction of losses and the ability to assemble and repair easily.
:Cut Core Transformer
This transformer has a core that is made of a cut piece of steel. Cut core is used to reduce losses and increase efficiency, especially in small and light transformers.
:Shell Core Transformer
In this type of transformer, the core is designed in such a way that the windings are placed inside a core shell. This design causes the magnetic field to be completely concentrated in the core and the magnetic losses are reduced. This type of transformer is used in applications that require high efficiency and loss reduction.
: Transformer with core (R) (R-Core Transformer)
The core of this transformer is circular in shape and has an R cross section. This type of core is used in precise and sensitive electronic equipment due to its excellent magnetic properties and loss reduction.
These different core designs give the transformer special characteristics that are selected and used depending on the specific application needs. Each type of core can affect the performance, dimensions, weight and cost of the transformer.
: Transformer with E and I core or armored (E-I Core Transformer)
In this type of transformer, the core consists of E and I-shaped metal sheets that are placed alternately on top of each other, and its general shape is rectangular. This design is one of the most common core types in transformers due to its simplicity and efficiency, and is used in many industrial and domestic applications.

:Transformers are divided into two main categories based on the number of phases
: Single-Phase Transformer
Definition: This type of transformer converts only one phase of alternating current (AC). It includes two primary and secondary coils that are connected to one phase of the power grid.
Applications: Single-phase transformers are commonly used in home, small business, and electronic equipment applications such as chargers, power supplies, and lighting systems. They are also used in electricity distribution for residential areas that use single-phase electricity.
: Three-Phase Transformer
Definition: This type of transformer is designed to convert and transmit electrical energy in three-phase systems. It consists of three primary coils and three secondary coils that are connected to three phases of the power grid.
Applications: Due to their high efficiency, three-phase transformers are used in industrial applications, large-scale power transmission and distribution, and large machinery such as three-phase motors, pumps, and compressors. They are also used in main power grids to supply electricity to large and industrial areas.
: Transformers are divided into various categories based on different applications. Below are some of these types
: Power Transformer
This type of transformer is used to transfer electrical energy at high voltages between different parts of the power grid. It is usually used in power plants and power stations.
: Distribution Transformer
These transformers are used to step down the transmission voltage and distribute energy to end users such as homes and businesses.
: Measuring transformer (Instrument Transformer)
This category includes current transformers (CT) and voltage transformers (VT), which are used to measure and monitor electrical parameters such as current and voltage in power systems.
: Isolation Transformer
This type of transformer is used to isolate different parts of an electrical system to prevent noise transmission and increase safety.
: Welding Transformer
This transformer is used in welding machines and converts the input voltage into low voltage and high current which is suitable for welding.
: Electronic Transformer
This transformer is used in small and light electronic devices and is usually used in high frequency circuits.
: Pulse Transformer
This type of transformer is used in pulsed applications such as radars, telecommunication equipment and digital systems and transmits high precision pulsed signals.
: Three-Phase Transformer
This transformer is used to convert three-phase electrical energy and is usually used in industrial power networks.
: Regulating Transformer
This type of transformer is used to adjust and stabilize the voltage at a certain level and is used in power systems that require stable voltage.
: Frequency Transformer
This transformer is used to change the frequency of electric current and is used in special industrial and military applications.
Each of these transformers are designed for specific applications and are used in different sectors of industry and power systems.
.jpg)
Transformers play an essential role in the supply and distribution of electrical energy in various industries and daily life due to their ability to convert and regulate electrical voltage. From energy transmission and distribution to industrial, domestic and commercial applications, transformers are considered as one of the key components of electrical and electronic systems. Choosing the right type of transformer for specific applications can help improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Electric energy transmission and distribution:
Transformers play a vital role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy from power plants to end consumers: Power transformers are used to increase the voltage of electricity produced in power plants to high voltages in order to reduce losses during transmission over long distances. Distribution transformers are used to reduce the voltage of electricity to a level Can be used in homes, offices and industries.
Manufacturing industries and factories:
Transformers are used in various industries to supply electricity to machinery and industrial equipment:
Furnace transformers are used to supply electric furnaces in steel and metalworking industries.
High frequency transformers are used in switching power supply systems and telecommunication equipment to change the frequency of electricity.
Telecommunication and electronic systems:
:Transformers play an important role in telecommunication and electronic equipment
Impedance matching transformers are used to match the impedance between sources and loads for optimal power transfer.
Isolation transformers are used for electrical isolation of different parts of a system in order to reduce noise and electromagnetic interference

Measurement and protection: instrument transformers are used in electrical measurement and protection systems:
Current transformers (CTs) are used to measure high currents and protect equipment against excess currents.
Voltage transformers (PTs) are used to measure high voltages in power systems.
Household and commercial applications: Transformers are used in many household and commercial appliances
Small transformers are used in electronic devices such as mobile phone chargers, televisions, computers and audio systems. Step-down transformers are used to reduce the input voltage to a safe level suitable for use in household appliances and office equipment.
Power supplies and UPS: Transformers are used in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems and power supplies to provide stable power